California’s rental housing market is dynamic, and landlords must stay updated with legal changes to remain compliant and avoid costly disputes. The year 2025 brings several new regulations that affect both landlords and tenants, from rent caps to eviction protections. Understanding these updates is essential for managing properties legally and maintaining strong tenant relationships.
Rent Control and Rent Cap Adjustments
One of the most significant updates in 2025 relates to rent caps under California’s Tenant Protection Act (AB 1482). The annual rent increase is now tied more closely to inflation, with updated limits set by the state. For most properties built before 2005, landlords cannot raise rent by more than 5% plus the local CPI (Consumer Price Index), up to a maximum of 10% per year. Staying aware of these caps ensures compliance and prevents disputes over unlawful rent hikes.
Just Cause Eviction Protections
California law continues to expand tenant protections around evictions. Landlords must provide a “just cause” reason for ending most tenancies, even after a fixed-term lease ends. Valid reasons include nonpayment of rent, significant lease violations, or the landlord’s intent to occupy the unit themselves. Without a just cause, tenants cannot be forced to vacate. These protections apply to many rental units statewide, so landlords must review their leases carefully and document any issues thoroughly.
Security Deposit Reform
In 2025, new rules around security deposits have been introduced to provide tenants with greater financial flexibility.
- Most landlords are now limited to collecting no more than one month’s rent as a security deposit for unfurnished units.
- For furnished units, the maximum is two months’ rent.
- Landlords must return deposits within 21 days, along with an itemized statement of deductions.
This change makes rental housing more accessible for tenants, but it also requires landlords to adjust their budgeting for turnovers and repairs.
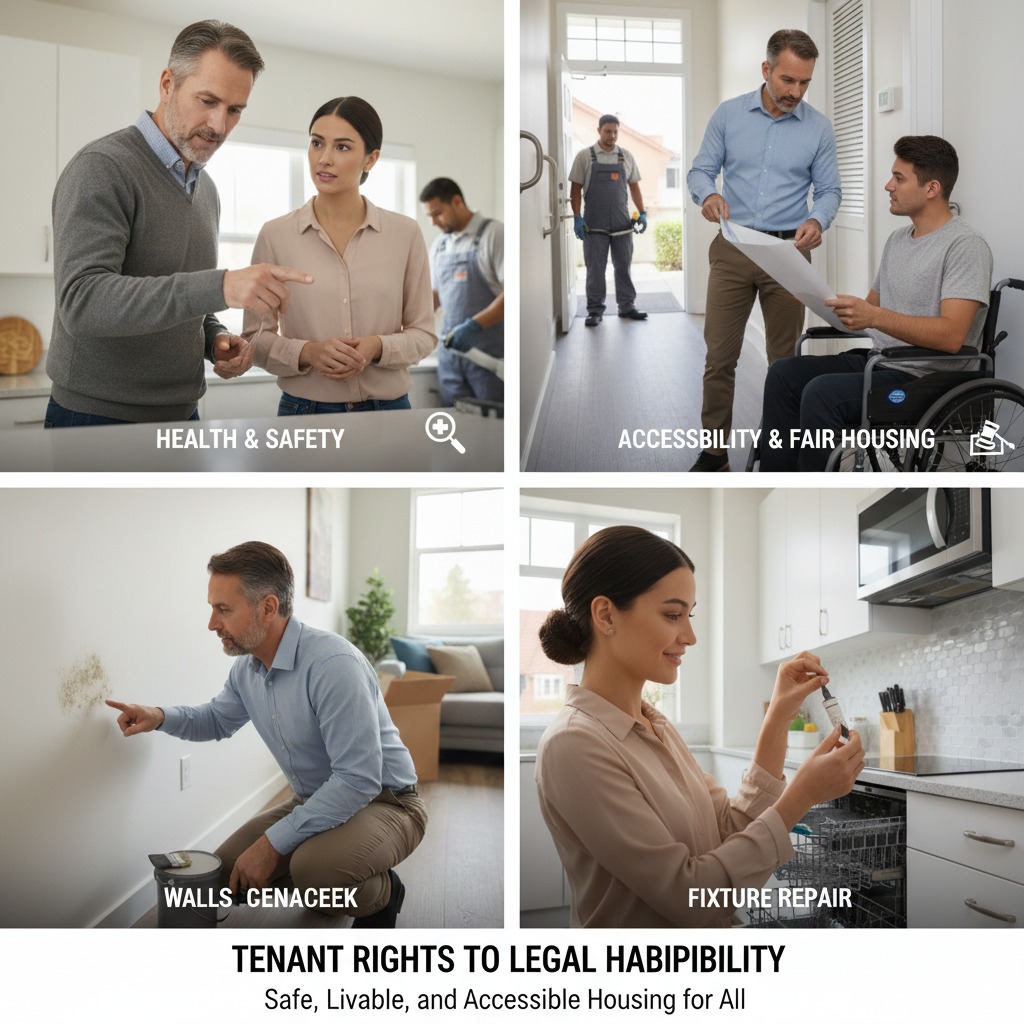
Tenant Rights to Habitability
The state has strengthened enforcement around habitability standards, ensuring tenants have safe and livable housing.
1. Health and Safety Requirements
Landlords must address health hazards such as mold, pest infestations, and broken heating systems more quickly than before. Failure to do so could result in fines or tenant claims.
2. Accessibility Improvements
There is also a growing emphasis on accessibility compliance. Landlords of multi-unit properties may be required to make reasonable accommodations or modifications for tenants with disabilities, in line with updated fair housing guidelines.

Short-Term Rental Regulations
Cities across California are tightening rules on short-term rentals like Airbnb. In many municipalities, landlords must now register short-term rental units, pay transient occupancy taxes, and comply with stricter zoning restrictions. For landlords considering renting units for fewer than 30 days, it is important to review local ordinances carefully, as rules vary widely between cities.
Digital Communication and Notices
California has also recognized the role of digital communication in modern property management. Starting in 2025, landlords and tenants may agree to deliver certain notices electronically, provided both parties consent in writing. While some notices (such as termination of tenancy) must still be delivered in person or by mail, digital notices can streamline communication for routine matters like inspection scheduling or maintenance updates.
Conclusion
The 2025 updates to California rental housing law highlight the state’s continued focus on tenant protections, affordability, and housing safety. For landlords, this means keeping leases up to date, adjusting financial planning around deposits and rent caps, and maintaining proactive communication with tenants.